COMPUTER Computer Format Kaise Kare | कंप्यूटर फॉर्मॅट कैसे करे | Step By Step
Dosto! Kaise ho aap log? Ummid karte hain thik hi honge, aur hum chahte hain ki aap log aur bhi zada acche rahe aur aap logo ka gyan din pratidin progress hote rahe. Aaj ke iss lekh main hum aap logo ko yeh batayenge ki Computer Format Kaise Kare. Computer toh aaj kal har koi hi use karta hain. Aur aaj ke iss advance jamane main har kisike paas har tarah ki jankari rakhna bahut zaruri hota hain. Aaj ke iss lekh main aap logo ko yeh acchi tarah se pata chal jayega ki computer ko format kaise kiya jata hain. Aap logo se humari bas yahi request hain ki aap log humare iss lekh ko dhyan se read kariye aur acchi tarah se yaad kar lijiye taki kabhi bhi aap log apne computer ko bina kisiki help liye format kar sake.
Computer Format Kaise Kare – कंप्यूटर फॉर्मॅट
Aajal ke nirantar badaltey pratiyogi mahaul mai computer ki mehatta se koi anjaan nahi hai. Ek safal career ke liye computer ka hona pehli aavashyakta hai. Lekin ussey bhi zyada zaroori hai computer ka sahi sthiti mai hona. Computer formatting karke aap apne system ko durust rakh saktey hai taki, kisi takniki mushkil ke karan aap or apke safal bhavishya ke beech koi rukawat na aaye. Kyuki kismet or waqt ruke hue logo ke liye nahi ruktey. Or ussey bhi badi takleef tab hoti hai jab aap apne computer mai aaye din aaney wali takniki dikkaton ke karan apne pratiyogi se peechey reh jatey hain. To chaliye jaane Computer Format Kaise Kare.
Computer ko format karne ke liye windows 7/windows 8 ka format disc (Bootable DVD) hona chahiye. Agar aapke paas nahi hain toh aap market se banva sakte hain ya online bhi download kar sakte hain. Format karne se pahle aap apne zaruri files ka backup zarur bana le. Ab aap log niche diye gaye steps ko follow kariye.
Step 1:
Windows 7/windows 8 ke format disc(Bootable DVD) ko CD/DVD Rome main dale aur computer ko restart kare.
Step 2:
Ab jaise hi aapka computer ya laptop restart hoker on hoga wese hi aapko enter press karna hain 4 se 5 baar. Uske baad aapka booting process automatic start ho jayega. Agar aapka booting process automatic start na ho raha ho toh uska dusra tarika bhi hain.
Dusra tarika – Jab aapka computer restart hokar on hoga wese hi aap TAB+F12, F10 ya F8 press kare. Fir CD/DVD Rome boot select kare fir 4 se 5 baar enter press kare. Uske baad window is loading file dikhayi dekha aur booting process shuru ho jayega.
Step 3:
Language select par click kare aur niche next par click kare.
Step 4:
Ab aap log Install par click kar de.
Step 5:
Apna operating system chune jo aapka computer ya laptop support karta ho. Ab aap log next par click kar dijiye.
Step 6:
Ab jo terms diye gaye hain unko except kare aur fir next par click kar de.
Step 7:
System partition C drive ko select kare aur fir drive option (advance) par click kar de.
Step 8:
Format option par click karke format kar de. Uske baad next par click kar de.
Step 9:
Ab operating system installation start ho jayega.
Jab yeh 100% ho jayega tab aapka computer automatic restart ho jayega.
Step 10:
Ab aapko apne system ka username daalna hain jo bhi aap rakhna chahte hain.
Step 11:
Ab aapko ask me later par click karna hain. Uske baad aapko time aur date set karna hain.
Congratulations! Aapka computer ab successfully format ho chuka hain.
Lekin ab aap log dekhenge ki aapke computer par sirf recycle bin ka hi shortcut aa raha hain. Toh ab aapko My computer, user profile shortcut apne desktop par lana hain.
Toh chaliye ab hum yeh jante hain ki desktop par shortcut kaise laya jata hain.
Sabse pahle apne mouse se right click karke personalisation option par click kar de.
Personalisation main upar change Desktop Icon par click kare.
Ab shortcuts ko select kare aur fir ok kar de.
Itna kaam karne ke baad shortcut aapke desktop par aa jayega.
Kuch aur tips
Yaha computer formatting ko assan shabdo mai samjhaya gaya hai, jissey aap khud bhi apne system ko format kaar saktey hain.
1. Sabse pehle to, computer format karney se pehley apne data ka backup zaroor rakh lein kyuki formatin ke waqt system mai maujood sara data delete ho jata hai.
2. Microsoft office ke jis version ko aap install karna chahtey hain us version ki bootable cd aapke pas honi chahiye. Ya to aap pendrive lagake bhi format kar sakte hai ya fir external hard disk lagake bhi format ho sakta hai.
3. Is cd ko cd drive mai daaliye aur apne computer ko restart kare or setup/installation start karney ke liye keyboard per ‘escape’ ya ‘f10’ key press kariye. Uske bade apko dekhaga ke file load ho raha hai. Iske bade aap thoda integar kare fir apko dusre area ke screen me alag alag ke file upload hote dekhayedenge. Iske baad apko windows ka install now option dekhega. Aap enter karke instaltion prakriyaa arambh kar sakte hai. Aap apna operating system ka chayan kare jo bhi operating system support karta hai apke anusar, iske uprante aap I agree button ka chayen kare.
4. Iske baad ek window open hogi jisme aap apne anusaar drive ki sankhya or size nirdharit kar saktey hain. Udahran ke liye – agar apke computer ka kul space 120 gb hai to aap ye space alag alag drive mai apni iccha anusaar vitarit kar saktey hain. Aam taur per c drive ko sabse zyada jagah di jati hai kyuki usme computer ke operating system ke saarey software ki files hoti hain. Iske alawa, yadi hum kisi or tarah ka software install kartey hain to wo bhi isi drive mai jata hai. Iske bade apko instialling window ka option dekhega and window is uploading file and percent kitna hua who bhi dekhega. Jab yeah 100 percent ho jayega to apka computer khud se restart hoga. Computer ka username apne hisab ke rakh sakte hai.
5. Iske baad apki screen per computer format karney ke vibhinn prakar ke tarikey dikhengey jaise format using fat (quick), format using ntfs (quick), format using fat, format using ntfs. Isme se aap apni iccha anusar kisi bhi ek format ka chayan karkey format kar saktey hain.
6. Ye ho janey ke baad apka system do se teen baar restart hoga. Uskey baad apko window ka screen dikhega jisme apko din, samaya or sthan ka vivran dena hoga. Iskey usprant apko ek username or password nirdharit karna hota hai.
7. Aap iske bad apne computer ka icon apne hesab se chayan kar kaun sa bhi photo ya widget rakh sakte hai. Aap apne computer ko pura customerise kar apne jaruat ke hesab se look de sakte hai jaise apne mane pasand ke wallpaper, screensaver and font and style badal sakte hai.
Upar diye gaye vivaran ke anusaar aap apne computer ko aasani se format kar saktey hain jiss se apka system bhi bina kisi dikkat ke chal sakey or apka kaam bina rukawat ke pura ho sakey. Computer format karne se to job he apke system me virus ya cache files hote hai who hat jata hai. Jiske wajah se apke computer ko nuksan bhi pahuch sakta hai and apke karya karne ke kshamta ko bhi dhimaa karta hai jaise pareshaniya se nejat dela deta hai. Format karne se aap bahut aasani se updated version ka bhi istemal kar sakte hai. Iske liye apka computer expert hona zaroori nahi hai, aap khud hi isme maharat haasil kar saktey hain.
Toh abhi tak toh aap logo ko yeh acchi tarah se samajh main aa chuka hoga ki hum apne computer ko format kaise kar sakte hain. Toh ab deri kaisi, inn naye naye tricks ko roj roj ajmate rahiye aur apne gyan ke bhandar ko roj roj aur bhi ujjwal karte rahiye.

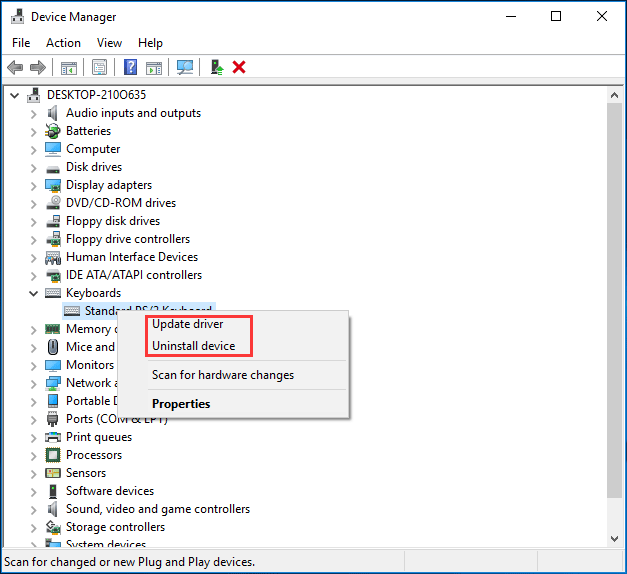



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/muted-speakers-annotated-262638f5f77f4ded9a65b949e726ec6a.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/playback-setting-annotated-fcb8c56d027748eab57d0013ba709396.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/troubleshooter-bad-annotated-ca677fc416c74f0d8ae45c3caf879309.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/enhancements-annotated-c6f71b4b33cd4950829ff1b3fc79f7e8.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/updatedriver-annotated-1d058482a2354b09bbcc22d85c5f76e3.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/registry-annotated-2d87ad5a4cb447058597da00ffa11dfc.jpg)
